According to data from market research institutions, the wearable market maintained a small growth in 2016, while smart watch shipments declined but smart bracelets continued to grow. Insiders say that one of the keys to the growth of the wearable market is the sensor. This article will introduce the types of sensors in wearable devices, as well as the importance of wearable sensors for wearable devices.
Market research shows that the wearable device market will reach 123 million in 2016 and 411 million in 2020. In the wearable device market, although the initial growth of the market is gratifying, the overall size of the wearable market is still relatively small worldwide compared to the smartphone market with annual shipments of more than one billion.

Schematic diagram of forecasting various types of wearable equipment market by foreign market agencies in 2020, data map
What sensors are in the wearable device? Sport sensorMotion sensors include: gyroscopes, accelerometers, pressure sensors, and magnetometers. Mainly used in equipment such as wristbands, their overall main function is to complete motion monitoring, navigation and human-computer interaction in smart devices. By recording and analyzing human activity anywhere, anytime with a motion sensor, users can know the number of steps they are running, the distance they ride, the time spent sleeping, and the energy consumption.
Gyro
These sensors improve the accuracy of motion and activity tracking. In general, the greater the number of gyroscopes, the better the results.
Accelerometer
In wearable devices, accelerometers can often be used to determine your steps and sleep quality. By measuring your movement speed, the accelerometer can "tell" the wearable device how far you have gone. If your wrist has not been moving, it will think you are asleep.
The biosensor includes a blood glucose sensor, a blood pressure sensor, an electrocardiographic sensor, a body temperature sensor, a brain wave sensor, a myoelectric sensor, and the like. Mainly used in medical electronic equipment, such as Kangkang sphygmomanometer, using human body signals collected by biosensors, through signal processing to complete health warning and disease monitoring functions. With these medical smart devices, doctors can improve their diagnostics and their families can communicate better with patients.
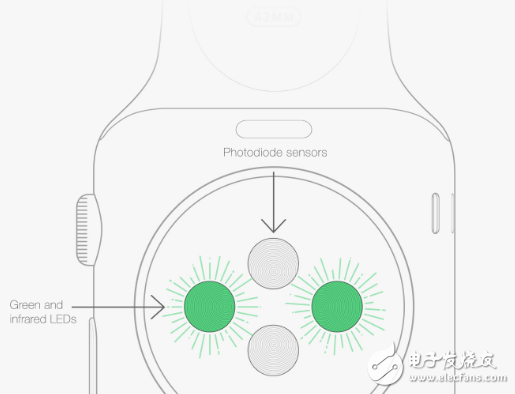
Optical heart rate monitoring
This device is located on your wrist and usually uses a red or green spot to detect your heart rate. This technology has been around for a while, but it was applied to wearables soon, mainly for sports enthusiasts, which allowed us to wave goodbye to the bulky chest strap heart rate sensor.
Environmental sensorEnvironmental sensors include temperature and humidity sensors, ultraviolet sensors, particulate matter sensors, gas sensors, pH sensors, air pressure sensors, etc., which can be used in PM2.5 portable detectors, AirWaves masks, portable personal integrated environmental monitoring terminals, etc. Environmental monitoring, weather forecasts and health reminders.
In fact, we are often in some environment that is harmful to health, such as air pollution, water pollution, light pollution, extreme weather, electromagnetic radiation, etc. What is even more terrifying is that we are often in such an environment without knowing it, not taking it. Effective defense measures have caused various chronic diseases for a long time, so environmental sensors have great market development potential and application value.
Barometer
This handy little device can tell you whether it is rainy or sunny today. These sensors are often used in sports wearables.
Alternative sensorAlternative sensors are mainly electronic skin, smart contact lenses and pH capsules. The electronic skin is embedded in a film that is smaller than the diameter of the human hair, and then placed in a polyester liner to monitor the patient's heart rate, body temperature, muscle activity and brain waves, and release heat to help the wound heal.
How important is the wearable sensor?The importance of sports, environment and biosensors
The earliest wearable device was a simple pedometer based on a three-axis accelerometer. Subsequently, complex devices including sensor components such as pressure sensors and gyroscopes soon appeared on the market. These devices enable wearable devices to identify the type of activity the wearer is participating in, such as walking, running, climbing, etc., and tracking their sleep cycles. At the same time, the temperature and humidity sensors enable the wearable device to more accurately measure parameters such as calories burned during exercise.
This trend of integrating more sensors into wearable devices will accelerate in the next few years. In particular, we will see more and more integrated motion and environmental sensors, as well as emerging biosensors. Biosensors are now available in stand-alone wearable medical monitors, and many consumer devices now offer heart rate measurement. But in the next few years, consumer devices will integrate a wider range of biosensors, such as spectral sensors that measure blood oxygenation, blood pressure and blood sugar levels, and skin resistance sensors that determine sweat levels and pH.
Advantages of integrating more sensors
The obvious advantage of integrating more sensors is that it increases the functionality of the device, allowing it to measure more parameters. In addition, the accuracy of the collected data can be improved.
For example, using information from other sensors to determine the type of activity the wearer is engaged in helps to select a more appropriate algorithm to process input from the acceleration sensor, making activity tracking more accurate. In addition, combined with data from numerous sensors, the device can extract more useful information to the user, for example, using heart rate, acceleration sensor data, and skin resistance sensing to measure a person's stress level.
Microphone component
In addition to the motion, environment and biosensors mentioned above, it is also possible for wearable devices to increase the use of microphone sensing elements. But the goal is not to provide the wearer with more information, but to help the device perceive its usage context in order to determine what information is useful to the wearer and how to deliver the information in an optimal manner. For example, if the device hears the roar of a jet engine, it can infer that the wearer is flying, monitor how long it has been sitting, and then adjust the recommendations for sleep and exercise to help the wearer cope more effectively with fatigue and dehydration. And time difference reaction.
Photovoltaic Single-Axis Tracking Bracket
Photovoltaic Single-Axis Tracking Bracket,One Axis Solar Tracker Solar,Solar Tracker Solar Racking Tracker,Solar Racking Tracker System Single-Axis
Hebei Shuobiao New Energy Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.pvbracketsystem.com
