The core value of the smart grid is to improve energy efficiency, use various high-tech methods to improve the operation and management level of each link of power generation, transmission, distribution, and power consumption, save resources and protect the environment; the smart grid is more suitable for multiple energy units for power generation, distribution, The need for electricity usage is more suitable for the market-oriented power trading needs, and is more suitable for customers' independent choices.
Electric vehicle to grid ( V2G ) technology is the two-way interaction and exchange of electric vehicle energy with the power grid in a controlled state. It is an important part of "smart grid technology" and applies V2G and smart grid technology. Therefore, the charging and discharging of electric vehicle batteries are deployed in a unified manner. According to the established charging and discharging strategy, on the premise of meeting the driving needs of electric vehicle users, the surplus electric energy is controlled and fed back to the power grid in two directions.
1 V2G system information flow
V2G embodies energy bidirectional, real-time, controllable, and flows between the vehicle and the grid.The charge and discharge control device has both interaction with the grid and interaction with the vehicle.The interaction content includes energy conversion information, customer demand information, Power grid status, vehicle information, metering and billing information, etc. Therefore, V2G is a high-end comprehensive application of many technologies such as power electronics, communication, dispatching and metering, and demand-side management.
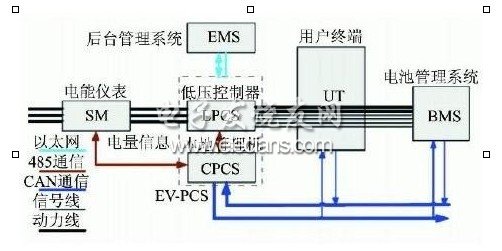
Figure 1 shows the V2G system information map
SM: Smart electricity meter, two-way measurement, local information storage, RS485 communication with EV2PCS, and transmission of power information to UT through EV2PCS;
EV2PCS: Two-way intelligent charge and discharge device, composed of a low-voltage controller and a local management machine, used to achieve two-way energy interaction between the vehicle and the power grid, is a key device of the V2G system;
UT: Human-computer interactive terminal, which is the interface between electric vehicle users and the grid, from which users obtain information on electricity consumption and electricity charges;
BMS: battery management system, used for the collection and transmission of vehicle battery data, monitoring of battery operating status, communication with EV2PCS via CAN bus, and transmission of vehicle information to the background through EV2PCS;
EMS: background management system, communicate with the grid dispatching system on the upper side, obtain grid load information and execute grid dispatching instructions, communicate with the EV2PCS on the lower side, obtain vehicle status information, and allocate and dispatch the power generation network dispatching instructions.
2 V2G system components
2. 1 two-way intelligent charge and discharge device
As a key power component in V2G technology, the two-way intelligent control device is used to realize the two-way flow of energy between the power grid and electric vehicles.It can work in charging mode and V2G mode: if you select the charging working mode, you only charge the vehicle, not The vehicle battery energy is fed back to the grid; if the V2G operating mode is selected, the device will connect the vehicle to charge and discharge according to the upper and lower SOC thresholds of the vehicle selected by the user on the human-machine interactive terminal, or the default upper and lower SOC thresholds of the device The real-time capacity, controlled time and other information are provided to the background management system. The background management system issues a charge and discharge control command. The device performs charge and discharge operations according to the current SOC of the vehicle battery to achieve two-way flow of energy.
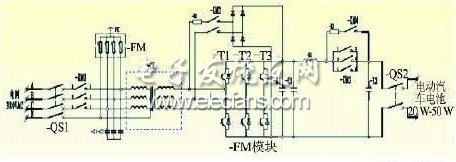
Figure 2 shows the main loop topology of the two-way intelligent control device
Its topological characteristics are as follows:
(1) The three-phase full-bridge two-way PWM conversion is used to charge and discharge the battery;
(2) The grid AC and the battery side of the electric vehicle are electrically isolated by an isolation transformer
(3) Simultaneous isolation transformer can perform voltage matching between AC and DC;
(4) The AC side and DC side are equipped with overload and overcurrent circuit breakers;
(5) The AC and DC sides are equipped with a pre-charging circuit, and the starting method is flexible;
(6) Adopt one-level converter, with simple topology and high reliability.
2. 2 Human-computer interactive terminal
The structure of the human-computer interactive terminal system is shown in Figure 3, which is mainly composed of an embedded controller, a touch screen, a radio frequency card reader, a CAN communication card, a remote monitoring and communication expansion card, and a micro printer. The main functions are: interface display, identification, EV2PCS control mode, ticket printing, data management and query, personalized parameter settings, language switching, and user operation assistance and abnormal information prompts.

Figure 3 shows the structure diagram of the human-computer interactive terminal system
What is a wireless AC controller? What does it do?
Wireless AC controller is a kind of network device, such as the AC100/150 of Fengrunda, which can be used to centrally control and manage wireless aps. It is the core of a wireless network and is responsible for managing all wireless aps in the wireless network. AP management includes: delivering configuration, modifying related configuration parameters, RF intelligent management, and access security control.
Why use a wireless controller, and what exactly does it do?
In fact, the role of the wireless controller is to play a gateway function between the WLAN and the Internet (on the router), and the data from different access points are aggregated and accessed to the Internet. The role of an access point (AP) is to complete wireless access, and it can control user access through network flags.
The role of wireless controllers
1, Flexible networking mode and excellent scalability
The AP does not need to be directly connected to the AC, so that the AP can be deployed in any place that needs to be covered through the network, such as you deploy an AP in each employee's home, and then connect to the wireless controller inside the enterprise through the VPN, you can expand the wireless network of the enterprise to the family of each enterprise member.
2, intelligent RF management functions, automatic deployment and fault recovery
Through the dedicated RF management module, we can initially estimate the AP deployment according to the user's architectural design drawing, and can calculate the average bandwidth of the wireless terminal, the coverage between AP and AP in the actual debugging process.
3. Centralized network management
All the configuration of the wireless network can be completed by configuring the wireless controller. For example, enable, manage, and maintain all AP devices and mobile terminals, including all functions such as radio wave spectrum, wireless security, access authentication, mobile roaming, and access users.
4, powerful roaming function support
The wireless controller uses AP as the boundary combined with fast RF management system, which greatly reduces the connection time between wireless client and AP, and thus realizes the function of fast roaming.
5. Load balancing
AP and wireless controller systems can distribute wireless users or terminals to nearby aps within the coverage area of an AP, ensuring the number of each wireless terminal or the sum of AP bandwidth transmission or the upper limit of each wireless terminal bandwidth.
6, wireless terminal positioning, rapid fault location and intrusion detection
Wireless controllers can track and locate the location of wireless terminals, such as wirelessly connected computers, PDAs and Wi-Fi mobile phones.
7, powerful access and security policy control
At present, the wireless system supports authentication of 802.1, WEB authentication, MAC, SSID, VPN, etc., and supports various encryption modes such as WEP, WPA, WPA-PSK, WPA2, etc., and all configurations can be configured globally through the wireless controller.
8, Qos support
AP and wireless switching systems can limit the maximum bandwidth of a user's wireless connection within each user's privileges. For different IP services, the system can also define different QoS queues through the wireless switch module. For example, for wireless voice applications, SIP and RTP protocols can be set in the high queue, while common applications such as http and ftp can be set in the low queue.
The wireless controller AC is more advanced than the AP, plays the role of manager in the wireless network, and the wireless controller AC also acts as a client to complete a series of functions in the wired network (such as authentication, authentication, etc.). However, wireless controller AC is not a WLAN device specified in the 802.11 protocol family, but as a supplement to the protocol in specific applications, and its price far exceeds that of ordinary access point (AP) devices.
In small-scale wireless networks that use only a few aps, it is not economical to use expensive wireless controller AC equipment. However, if the number of wireless aps is large, more than 20 can be used AC controller.
Ac Controller,Gigabit Wlan Controller,Enterprise Ac Gateway,Wireless Ap Controller
Shenzhen MovingComm Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.szmovingcomm.com
