Abstract: Based on the DSP development platform, this paper designs the communication program of the motor controller node of electric vehicle. In order to effectively monitor electric vehicles and various subsystems, an application layer protocol and monitoring system for the electric vehicle CAN bus was designed. Experiments show that the monitoring system can communicate with other nodes through the CAN bus, thus realizing real-time online data monitoring and fault diagnosis.
This article refers to the address: http://
Keywords: CAN bus; electric car; TMS320LF2407
Design and Development of a Test Platform for the Electric Vehicle
Yao Zhen Xie Guo-lin Li You-xin Liu Fang-ming
Luo Zhu-wen Deng Xian-quan
(1. Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, china,
510006; 2. Shenzhen Wuzhoulong Automobile Co., Ltd. Shenzhen,
Guangdong, china, 518116)
Abstract: Based on the DSP platform, the author designs a communication
Program for motor controller. In order to control and monitor the dynamic
System and other subsystems of an electric vehicle (EV) effective, the monitor
System and EV CAN bus application layer protocol are developed. It is proved in
The condition of lab that the monitor system can be used to communicate with
Other nodes of the car through the CAN bus so as to realize the on-line data
Monitoring and fault diagnosis.
Key Words: Controller Area Network, Electric Vehicle, TMS320LF2407
1 Introduction <br> There are many electronic control units in the electric vehicle, small internal space and large environmental interference, which puts higher requirements on the control system and communication system. With its excellent operating characteristics, high reliability and unique design, CAN is especially suitable for communication between electronic control units of electric vehicles. In order to better conduct research in the laboratory, a well-functioning test and test platform was established to study the CAN bus system and its network protocol. First, DSP-based development designed the communication program for the motor controller node. Secondly, to understand the application requirements of CAN bus in electric vehicles, design CAN
The application layer protocol of the bus. Finally, in order to verify the feasibility of the design agreement, the monitoring system of the electric vehicle was developed using VB6.0, and a database was established for the monitoring data to facilitate the management of data.
2 Motor controller node design
For the characteristics of electric motor controllers, TI's TMS320LF2407 chip is selected as the processor of the motor controller. Using a modular design concept, a communication program for the motor controller node is programmed for easy migration to a DSP-based motor controller or other control unit. In the CAN bus system of electric vehicles, the real-time requirements of the motor controller are high, belonging to high-speed nodes, and the baud rate is set to 1 megabaud. The motor controller node mainly receives the control information of the motor working mode, SOC, vehicle speed, accelerator pedal position and brake pedal position uploaded by the bus, and transmits real-time information such as working temperature, motor fault and working state of the motor. In this paper, the mailbox 2 of DSP2407 is used as the receiving mailbox, and the mailbox 5 is used as the sending mailbox, which is sent once every 20 milliseconds.
3 Electric vehicle monitoring system design
The electric vehicle CAN bus system is simulated in the laboratory, and the PC (with USB-CAN module) is used as the overall controller of the electric vehicle. Based on the operating mechanism and working principle of CAN-bus universal test software, the monitoring system of CAN bus technology based on PC is designed.
3.1 Overview of the monitoring system The monitoring system monitors the motor controller, battery controller and clutch controller via the console (PC with USB-CAN module). The main operation interface is shown in Figure 1. Can be as needed
Transceiver parameters in the CAN bus to monitor and control each node of the bus. For example, motor parameters,
Including SOC, vehicle speed, fault level, working mode, fault code, operating temperature, etc. The monitoring system also provides the ability to create nodes based on system expansion needs. In addition, data management functions are also available.
During the execution of the monitoring system, the collected data is recorded in the Microsoft Access database, can be displayed in real time in tabular form, and can be opened by software Excel through the output button.
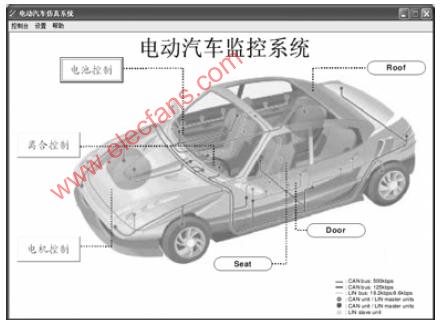
Figure 1 Electric vehicle monitoring system operation interface
3.2 Monitoring system communication protocol <br> Only two protocols of data link layer and physical layer are defined in the CAN protocol, which lacks the specification of information processing, and a complete network system cannot be separated from the application process of human-computer interaction. Therefore, the application layer protocol must be defined by the user. According to the characteristics of electric vehicle operation, the communication protocol of the monitoring system is designed. In general, each electronic control unit (ECU) on an electric vehicle is divided into two categories: high speed and low speed nodes. Among them, the high speed node includes motor controller, engine controller, battery controller, ABS/ASR
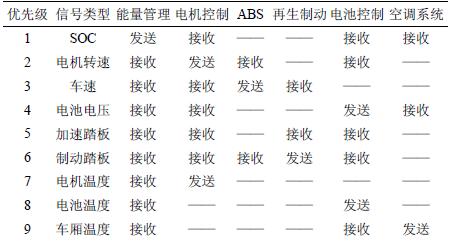
Control units and energy management units, etc., set a higher priority in their ID codes. The low speed node includes an air conditioning system, an instrument display system, a lamp system, and the like. Table 1 shows the types of signals received and transmitted between the nodes of an electric vehicle. The receive and transmit data between nodes of an electric vehicle, of the type of information to be exchanged between the nodes, and the parameters contained in the representation methods are specifically described. For example, the 8 bytes sent at the motor controller node are defined as: motor speed (double byte), motor torque (double byte), operating temperature (single byte), error level and code (single byte) The working mode (single byte) also has one byte as a spare. Table 1 shows the data received and sent between the nodes of the electric vehicle . For example, the 8 bytes sent at the motor controller node are defined as: motor speed (double byte), motor torque (double byte), operating temperature (single byte), error level and code (single byte) The working mode (single byte) also has one byte as a spare.
Table 1 Data received and transmitted between nodes of electric vehicles
3.3 Monitoring system program design The monitoring system is to complete the monitoring of each node. According to the design requirements, the whole design can be divided into five design forms, including main form, motor controller monitoring form, battery controller monitoring form. The clutch controller monitors the form and creates a node form and modularizes the design. The node form can be created to easily create a monitoring window, set the node ID number and monitor variables. The monitoring system programming flow chart is shown in Figure 2.
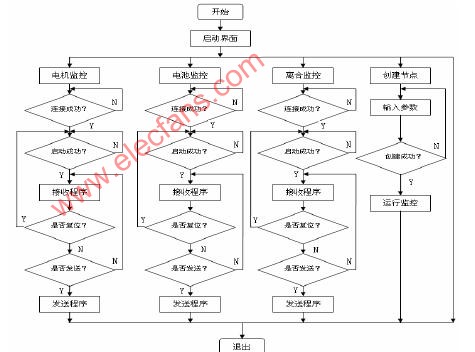
Figure 2 Monitoring system program flow chart
4 Monitoring system test <br> After completing the PC monitoring system program design, in order to verify the normal operation of the program, and in order to verify the correctness of the designed lower-end DSP data acquisition and communication program. Here, the DSP data acquisition is combined with the communication program and the PC program for debugging. Set the baud rate of both to 1M baud. The test program of the DSP node includes A/D sampling (analog accelerator pedal position) and communication program. After the DSP runs, the data is collected and processed by the timer interrupt (20ms), and the signal is uploaded to the host computer (PC) through the CAN bus. On the other hand, the DSP automatically determines if there are instructions from the PC, such as battery voltage, battery current, accelerator pedal position, and operating mode. After receiving the data, the host computer processes it and hands it to the monitoring system for display. The test interface of the motor controller node is shown in Figure 3.
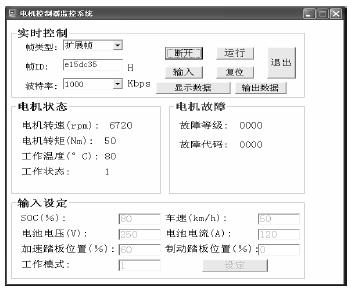
Figure 3 Test interface of the electric controller
5 Conclusions <br> In order to meet the needs of electric vehicle monitoring, a CAN bus-based electric vehicle simulation test platform has been set up, and a professional test instrument can be used to form a CAN-BUS laboratory. The system has good scalability and can easily increase the electronic control unit (ECU) of the car that needs to be monitored. In addition, through the good connection between VB and ACCESS technology, data is saved in real time, which provides conditions for later data processing. In order to ensure that each message can be collected and processed by related nodes in time, the scheduling strategy of the message needs to be deeply studied to further optimize network management, especially network fault diagnosis and processing mechanism.
Pp-Pe Film Pelletizing Line,Pelletizing Line For Pp-Pe Film,Pp-Pe Film Recycling Machine, Film Granulator For Pp-Pe
Zhejiang IET Intelligent Equipment Manufacturing Co.,Ltd , https://www.ietmachinery.com
