The transmission network is an important part of the communication network. Without it, data communication between different devices of the network is impossible.
Many students hope to understand and learn about the transmission network. However, for beginners, the most painful thing is the concept of dizzying people.

Today, I'm going to die, specifically introducing these common concepts and their relationships, hoping to help everyone have a preliminary understanding of the transmission network.
Overall structure
Transmission network this Eastern, there is a very flexible architecture design. In different application scenarios, the networking architecture may also be different. Moreover, not only telecom operators have a transmission network, such as electricity, oil, radio and television and other industries, but also have their own specialized transmission network.
The following is a transmission network architecture of a typical 2G mobile communication network:
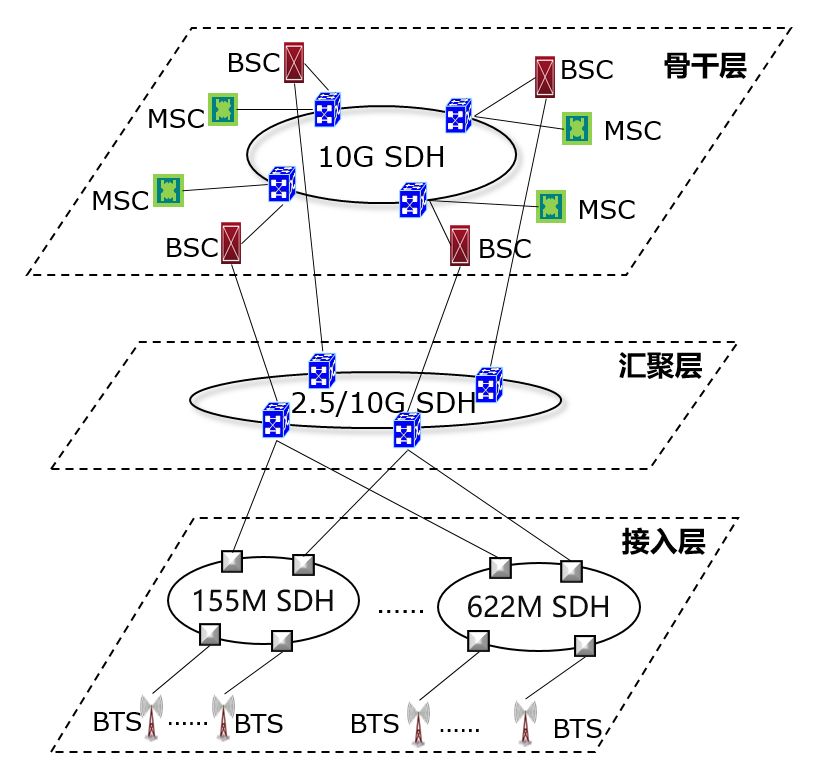
As can be seen from the figure, the transmission network is mainly divided into three layers: access layer, convergence layer, and backbone layer. Knowing their names can help them understand their role: Responsible for accessing customer-side services, responsible for service aggregation and uploading, and responsible for carrying traffic scheduling between the aggregation and core layers.
Why is each layer a ring network?
Mainly because of security protection, in the case of a ring network, it can withstand a single point of connection failure.


The E1 line is the 2M line (two mega lines) that we used to say.

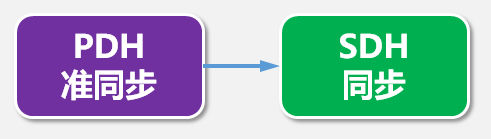
SDH (Synchronous Digital Series)
Well, since the front said "quasi-synchronous", the next step is "synchronous".
Because PDH can not meet the needs of the development of modern telecommunications, SDH was born.

Due to the many advantages of SDH, it was favored by global telecommunication operators and once dominated the transmission network.
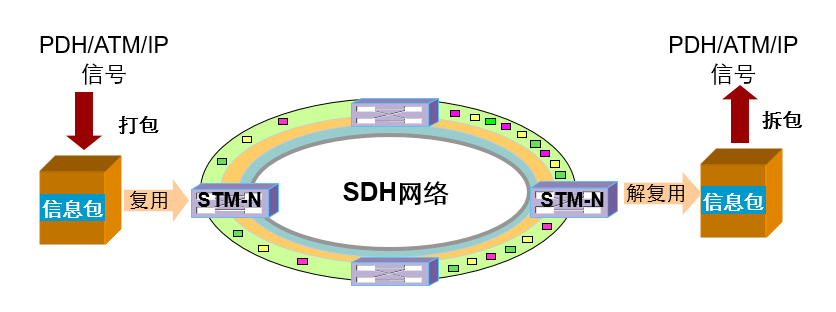
SDH work
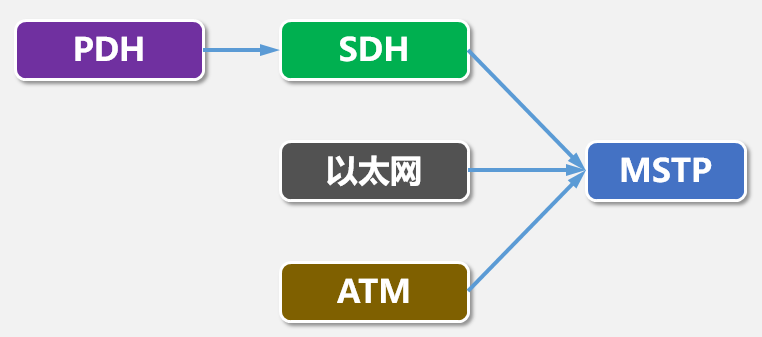
MSTP (Multi-Service Transport Platform)

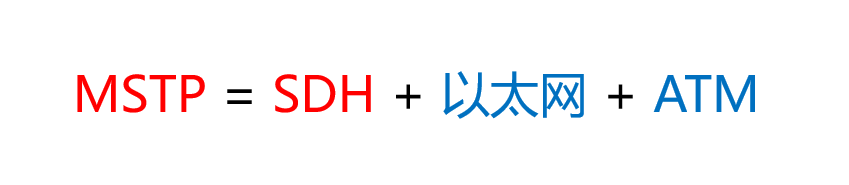
MSTP adds an Ethernet interface or an ATM interface to SDH to implement an IP interface.

MSTP device (you can see various interfaces such as Ethernet ports)
In summary, the relationship between PDH, SDH, and MSTP is as follows:
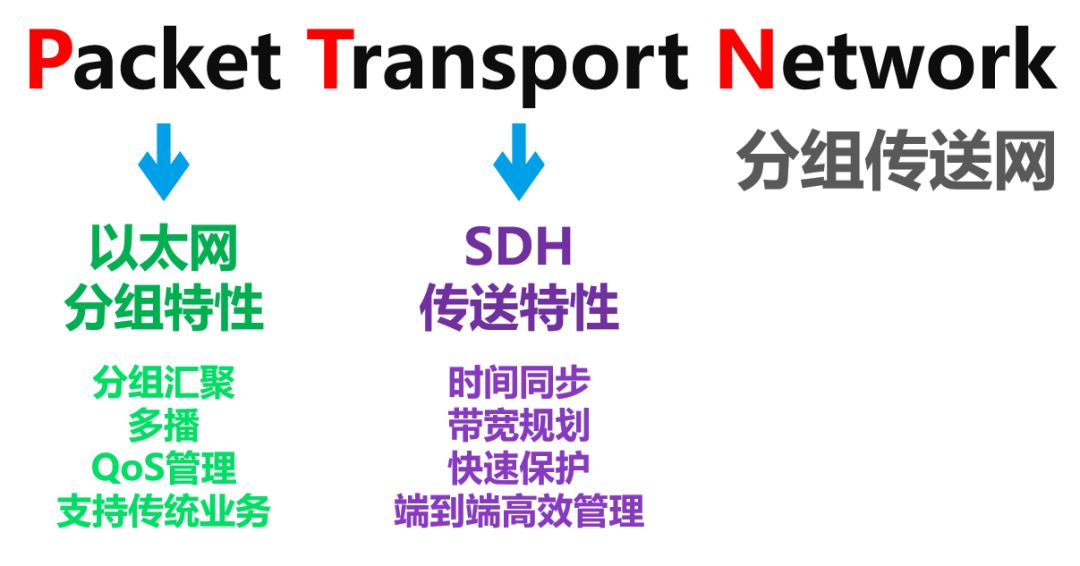
PTN (Packet Transport Network)
In any case, MSTP and SDH are based on Circuit Switching (TDM) and cannot carry data services (IP) better.
As we all know, with the development of communications, telecom services have become mainly Internet-based, and the proportion of data services has increased dramatically.
So, PTN appeared.
PTN, Packet Transport Network, packet transmission network.
From the perspective of the transmission unit, the smallest unit transmitted by the PTN is the IP packet, while the SDH transmits the time slot, and the minimum unit is the E1. The PTN packet size is flexible, while the SDH circuit bandwidth is fixed. This is the most essential difference between PTN and SDH.
Speaking of PTN, we must first explain MPLS.
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching)
MPLS, Multi-Protocol Label Switching, Multiprotocol Label Switching.
Multi-Protocol: Supports multiple Layer 3 protocols (IP, IPv6, IPX, SNA, etc.).
Label Switching: Labels packets and replaces IP forwarding with label switching.
In traditional IP networks, routing technologies are unmanageable and uncontrollable. IP is forwarded step by step, and each route through a router must be routed (possibly multiple times), which is slow. This type of forwarding mechanism is not suitable for large networks.
MPLS uses pre-assigned labels to establish a Label Forwarding Channel (LSP) for packets. At each device through which the channel passes, only a quick label exchange (one lookup) is required, saving processing time. time.
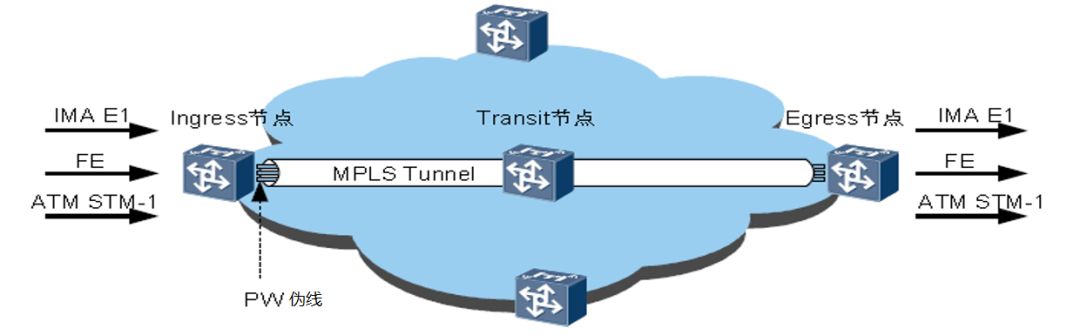
MPLS Tunnel
In simple terms, MPLS is faster, more efficient, and more suitable for high-capacity networks.
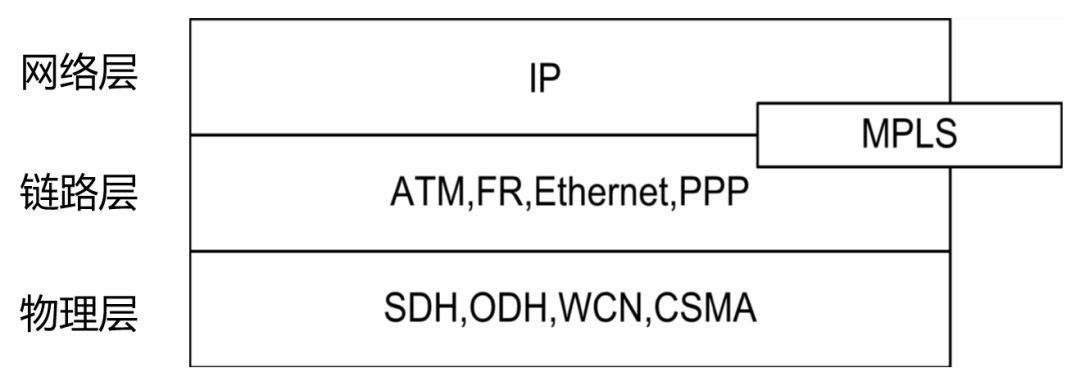
MPLS location in the protocol stack
T-MPLS, however, is an improved MPLS.
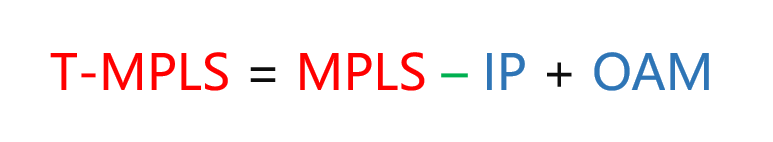
T-MPLS is a subset of MPLS. It uses only MPLS technology related to the data transmission layer, removes the complicated automatic routing protocol control technology at the network layer, and adds OAM (Operation Administration and Maintenance, that is, operation, management, and maintenance). ).
T-MPLS and MPLS-TP
In May 2005, ITU-T launched T-MPLS and succeeded in the market.
In 2007, the IETF began to obstruct the adoption of T-MPLS by ITU-T in the interests of interests.
In 2008, ITU-T and IETF jointly established JWT, a joint working group, and introduced MPLS-TP, which is positioned as the evolution of T-MPLS.
ITU-T: International Telecommunications Union Telecommunications Standards Branch
IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force
Therefore, using the PTN of T-MPLS, it has the basic characteristics of high speed and high efficiency.
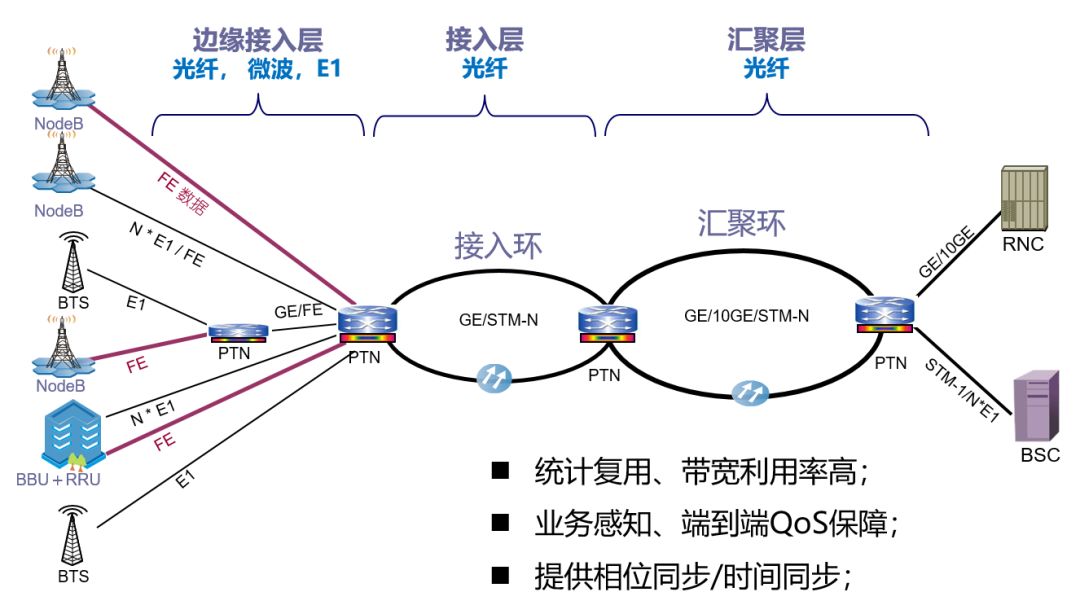
PTN in wireless access network
PTN, in a nutshell, is an enhanced IP network with SDH features that combines the advantages of the two.
After finishing PTN, we have to go back and talk about the "light" things.
WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing)
WDM, Wavelength Division Multiplexing, Wavelength Division Multiplexing.
In simple terms, WDM multiplexes optical signals of different wavelengths into the same fiber for transmission.
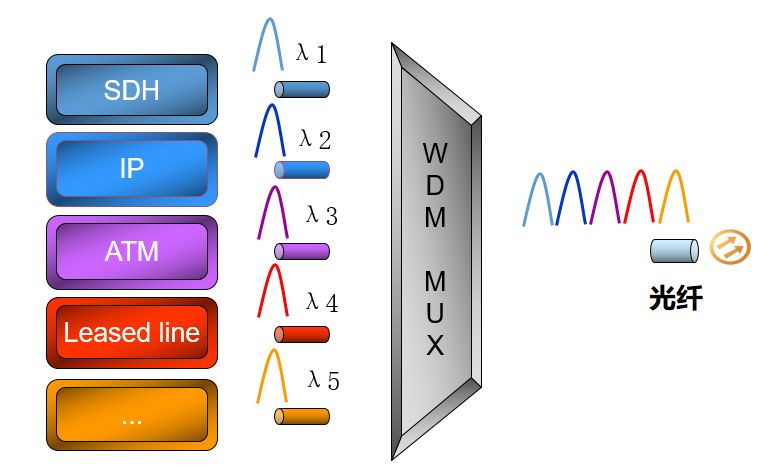
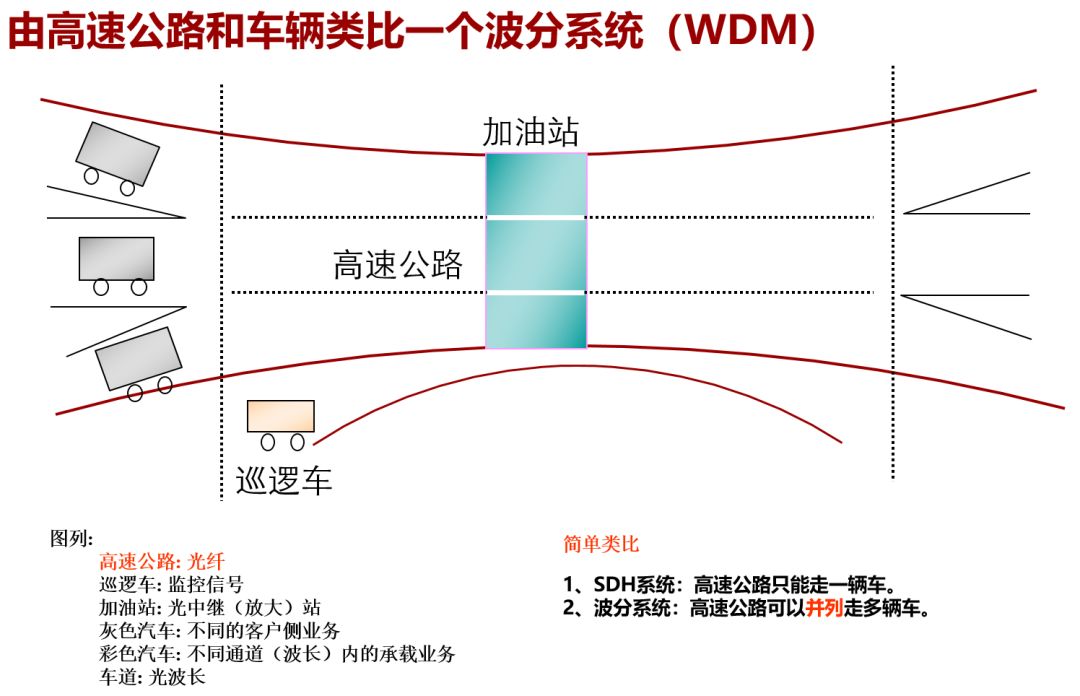
Wavelength division multiplexing and frequency division multiplexing
In fact, wavelength division multiplexing is a type of frequency division multiplexing. Wavelength × frequency = speed of light (fixed value), so the actual wavelength is divided by frequency. In optical communication, people are accustomed to naming by wavelength.
What we often call DWDM is dense WDM, Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing. DWDM is a specific form of WDM. In early WDM systems, the wavelength spacing was several tens of nanometers. Later, the wavelength spacing developed to a few nanometers was called DWDM.
Sparse wavelength division multiplexing (CWDM): large wavelength spacing, typically 20nm
Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM): small wavelength spacing, less than or equal to 0.8nm
The advantage of WDM is obvious, that is, it has a large capacity, and it can be transmitted over long distances.
However, WDM also has disadvantages. For example, it can only be connected point-to-point, cannot form a ring, cannot be flexibly scheduled, and cannot cope with complex networking structures.
However, SDH can be ah, SDH can form a ring, and management ability is very strong.
So, simply introduce SDH's features into WDM!
So, there is OTN.
OTN (Optical Transport Network)
OTN, Optical Transport Network, Optical Transport Network.
As mentioned earlier, it is based on WDM technology.
OTN integrates some advantages of SDH on WDM, such as abundant OAM overhead, flexible service scheduling, and perfect protection methods.

The OTN service scheduling is divided into:
Optical layer scheduling (can be understood as a category of WDM)
Electrical layer scheduling (can be understood as the scope of SDH)
OTN and PTN
Although there is only one word between OTN and PTN, both are completely different technologies.
PTN has a smaller transmission bandwidth than OTN. The maximum PTN bandwidth of the general group is 10G. OTN single-wave 10G, group road up to 400G-1600G, the latest technology can reach single-wave 40G.
OTN is the backbone of the transmission network.
PON (passive optical network)
Next, let's say a "fat" child, that is, PON (read "fat").
PON, Passive Optical Network, Passive Optical Network.
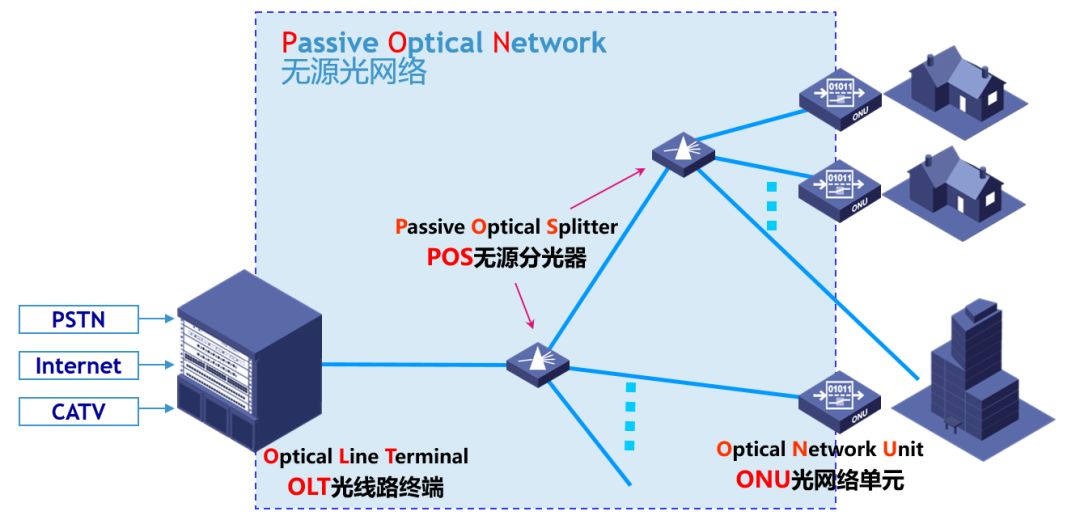
PON consists of the following components:
OLT (Optical Line Terminal)
POS (passive optical splitter)
ONU (Optical Network Unit)
Because the OLT and the ONU are passive, they are called "passive optical networks."
What is passive?
This "source" refers to the power source, energy source, and power source.
To put it plainly, no such "source" electronic device is called a passive device. To be simpler, under the passive network, what you are giving is no energy source for amplification or conversion.
The PON adopts the WDM technology and realizes bidirectional transmission of single fibers. The upstream wavelength is 1310 nm and the downstream wavelength is 1490 nm.
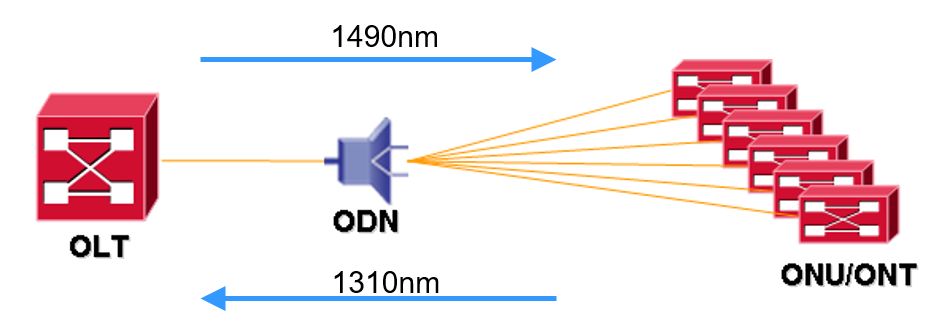
PON, with its many advantages, such as high bandwidth, high efficiency, large coverage, and rich user interfaces, is regarded as an ideal technology for broadband access and integrated transformation of access network services.
According to the content of the bearer, the PON is mainly divided into the following types:
ATM Based Passive Optical Network (APON)
Ethernet-based Ethernet Passive Optical Network (EPON)
Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) based on GFP (Generic Framing Procedure)
To add that, corresponding to the PON is AON, Active Optical Network, active optical network.
IPRAN (IP Access Network)
Let's talk about IPRAN, which is now very hot.
Over the years, the radio access network (RAN) has been developing towards full IP. Therefore, the traditional SDH transmission network cannot meet the requirements. We need an IP-based transmission network. The IP-based transport network is divided into IPRAN and PTNRAN.
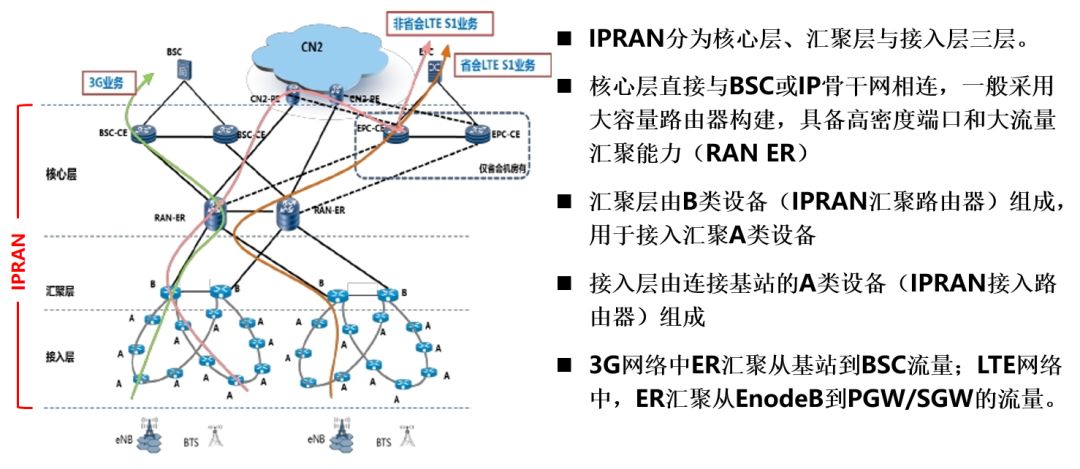
IPRAN example
We look at the advantages of IPRAN by comparing it with traditional RAN (based on MSTP).
MSTP is developed on the basis of SDH to meet data needs and is essentially a transmission. IPRAN is developed on the basis of routers to meet the needs of base station access. Essentially, it is a router that can satisfy integrated service access.
MSTP inherits the characteristics of SDH, rigid bandwidth, and all services use fixed bandwidth regardless of whether they are used. IPRAN is a feature of routers, sharing bandwidth, and sharing bandwidth between services. Shared bandwidth costs less.
MSTP mainly works on Layer 2. IPRAN mainly works on Layer 3 and can access Layer 2 services through service emulation.
MSTP is relatively rigid and all service flows must be specified manually. IPRAN is very flexible, and service flow can pass as long as there are routes.

Name of IPRAN
IP RAN, simply put, refers to IP-based mobile backhaul networks. The foreign name is actually more accurate: IP Mobile Backhual.
At the beginning, the industry proposed several ways to replace the traditional MSTP, Cisco proposed IP/MPLS mode, and named as IP RAN. This is exclusivity. Due to its strong position in the data communications industry, Cisco's naming method has naturally caused confusion in industry terms, so that the IP/MPLS-IP RAN bearer method is now commonly referred to as IP RAN.
ASON (Automatically Switched Optical Network)
The last one to introduce is ASON.
ASON, Automatically Switched Optical Network, Automatically Switched Optical Network.
The concept of ASON was proposed by the ITU in March 2000. The basic idea is to introduce a control plane in the optical transport network to realize the on-demand allocation of network resources so as to realize the intelligence of the optical network.
Simply put, it is to enable future optical transport networks to provide connectivity for any location and any user, a "smart" optical network.
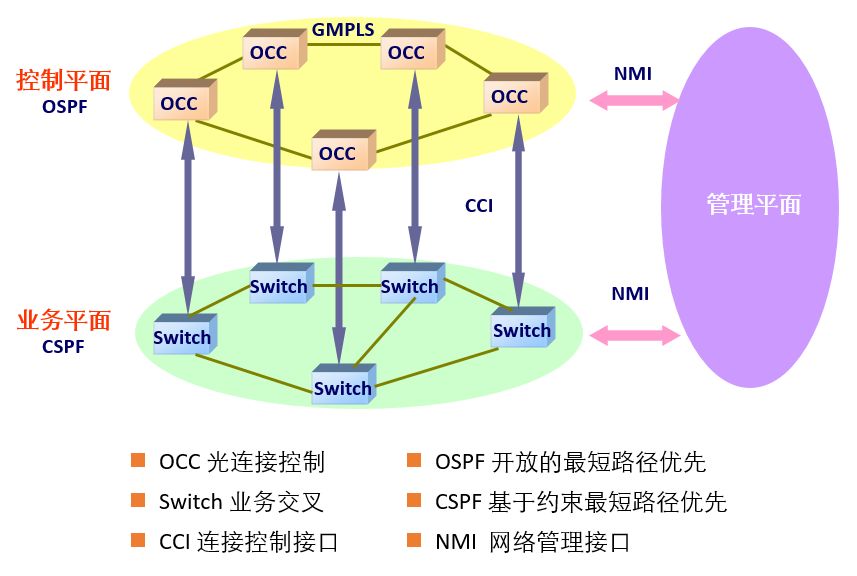
ASON architecture
The existing optical transport network cannot meet the requirements of communication operators for economical efficiency and high efficiency. ASON has the protection and recovery mechanisms that cannot be matched by traditional SDH networks and meets the needs of network development.
Therefore, the intelligent optical network represented by ASON will surely become the mainstream of the next-generation switching network.
Okay! Finally finished the presentation. . .
Do not know if you have not seen halo? Well, in fact, jujube monarch himself a little dizzy. . .
As the major artery of the communication network, the transmission network is indeed a top priority and its status is very important.
Because of this, operators and equipment vendors have high requirements for its stability, efficiency, and capacity. Therefore, it is constantly undergoing technological update iterations, and new products and concepts are emerging.
The utility model discloses an Electronic Cigarette with atomizer oil core separation structure, which comprises a atomizer assembly and a battery assembly; The utility model has the advantages of reasonable structure design and high practicability. During operation, because the oil storage tank of the atomizer is completely sealed and the oil guide material is completely isolated from the oil guide material, the oil guide material will never contact with the oil guide material in the storage process
Advantages:
Oil core separation, Mesh removable heating core, Ultra quiet design,100% oil leakage free, Excellent taste, Cost far less than the industry price.
A variety of colors and finishing are available, can be adjusted according to your market needs.
Oil Coil Separation Pod Patent,Oil Coil Separetion Vape Pod Oem,Innovated Vape Products Oem,Oil Coil Separation Vape Products Oem
Shenzhen MASON VAP Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.disposablevapepenfactory.com
