Charging this thing, the popular point is to feed the battery. Then you must first consider the battery feel. Take the current popular iphonexplus, Huawei P9, Le 2, Xiaomi note as an example, the battery capacity does not exceed 3000mAH. According to 4.35V as the highest voltage, the maximum possible charging power is about 20W in terms of 1.5C charging. Of course, this is the limit case. In addition to the power receiving capability, it also involves current acceptance. At 1.5C charging, the 3000mAH battery charging current will reach 4.5A, so the battery contacts and the current transfer structure inside the cell must be optimized.
Second: the power supply capability of the adapter20W power is a breeze for the adapter, regardless of the interface's ability to withstand. However, the traditional MicroUSB interface has a maximum current carrying capacity of 2A and a maximum voltage of 5.25V in the standard specification. Only 10.5W, can not meet the requirements of 20W. How to solve this problem? Obviously there are two solutions to increase the current or boost the voltage. If you do not change the physical interface, increasing the current is an impossible option, so boosting the voltage is the only option in the MicroUSB era, which is the origin of the Qualcomm QC fast charging method. Therefore, we can see that 1.5A is the recommended current for the QC standard. Because 2A is the limit of MicroUSB, the general consensus in the industry is not to use the device to the limit value, but to reserve the margin. In this regard, OPPO and Qualcomm have taken the opposite path. They have physically patched MicroUSB and added additional contact pins designed to transmit large currents. The maximum charging current reaches 4.5A, but the voltage remains at 5V. A power transfer of more than 20W is also achieved. The emergence of the Type-C interface makes this problem no longer exist, because the TYPE-C port supports up to 5A input current, which can fully meet the fast charging requirements of existing mobile phone batteries.
Third: mobile phone charging management and cooling capacityThe phone's charging management and cooling capabilities. Charging management, inevitably involves voltage conversion, constant current control and other links, resulting in a decline in charging efficiency and heat dissipation. Therefore, the theoretically optimal charging design is that the internal management of the mobile phone is not done, and it is completely handed over to the external adapter for control. At this point, QC is relatively disadvantageous, because the high voltage and low current input will inevitably lead to energy conversion inside the mobile phone, becoming low voltage and high current. This will cause a big problem with the cooling of the mobile phone. Therefore, from a technical point of view, the historical limitations of QC have been highlighted. A more serious problem is that it is strictly forbidden to adjust the charging voltage by means other than USBPD in both TYPE-C interface and USBPD. Qualcomm has made great efforts to persuade the USB-IF organization to try to make both QC and PD exist in the TYPE-C interface. However, unfortunately, it was relentlessly rejected, and the latest TYPE-C1.2 and USBPD3.0 maintain a description of this feature. Therefore, QC will face the danger of being eliminated both technically and theoretically. Of course, Qualcomm itself is very clear about this trend. Therefore, the negotiation function of USBPD has been integrated in the latest processor core.

The USB-PD communication is a process of modulating a protocol layer message into a 24 MHz FSK signal and coupling it to VBUS or obtaining an FSK signal from VBUS to implement communication between the handset and the charger.
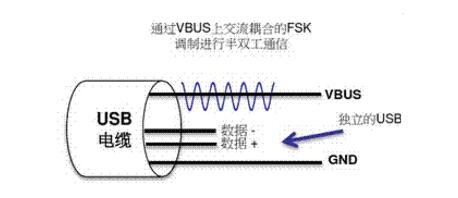
As shown in the figure, in USB-PD communication, the 24MHz FSK is coupled to the DC level on the VBUS through the cAC-Coupling coupling capacitor, and the 24MHz FSK is not generated for the Power Supply or USB Host VBUS DC voltage. The effect is that a low-pass filter consisting of a zIsolation inductor is added to the loop to filter out the FSK signal.
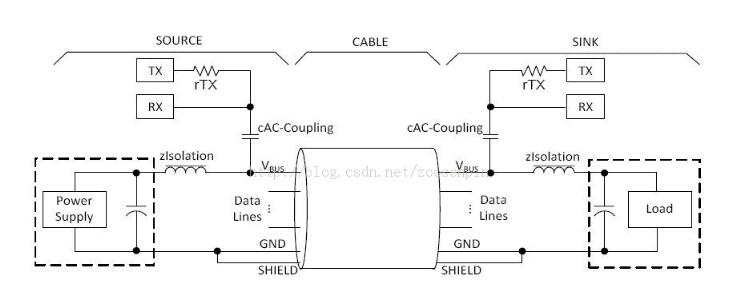
The principle of USB PD is as follows: The mobile phone and the charger support USB PD as an example:
1) USB-OTG PHY monitors VBUS voltage. If there is VBUS 5V voltage and it detects that OTG ID pin is 1K pull-down resistor (not OTG Host mode, OTG Host mode ID resistance is less than 1K), it means the cable Is supporting USB PD;
2) USB-OTG performs normal BCS V1.2 specification charger detection and starts USB PD device policy manager. The policy manager monitors whether the FSK signal is coupled to the DC level of VBUS, and decodes the message to obtain a CapabilitiesSource message. Parsing the message according to the USB PD specification yields a list of all voltages and currents supported by the USB PD charger;
3) The mobile phone selects a voltage and current pair from the CapabilitiesSource message according to the configuration of the user, and adds the voltage and current pairs to the payload of the Request message, and then the policy manager couples the FSK signal to the VBUS DC level;
4) The charger decodes the FSK signal and sends an Accept message to the mobile phone, and adjusts the DC voltage and current output of the Power Supply;
5) The mobile phone receives the Accept message and adjusts the charging voltage and current of the Charger IC;
6) The mobile phone can dynamically send a Request message during the charging process to request the charger to change the output voltage and current, thereby achieving a fast charging process.
QC3.0 Fast Charge Protocol CX7916 Overview:The CX7918/CX7916 is a USB mobile device charging interface control chip. In particular, it uses the Qualcomm QuickCharge 3.0A/Class B specification to adaptively charge HVDCP. The CX7918/CX7916 can accurately adjust the HVDCP output voltage based on the voltage request sent by the mobile device, saving up to 75% of the charging time.
When the mobile device is plugged into the USB port, the CX7918/CX7916 automatically recognizes its type and makes a reasonable response so that the mobile device always gets the maximum current from the charging port. The CX7918/CX7916 supports Apple iPad, AppleiPhone, SamsungGalaxyNote, BC1.2 or YD/T1591 compliant devices and almost all modern mobile devices. The CX7918/CX7916 will automatically detect whether the connected powered device is compatible with QC2.0 or QC3.0 protocol specifications before starting the output voltage adjustment. If the powered device is not compatible with QC2.0 or QC3.0 protocol, CX7918/CX7916 The output voltage adjustment is disabled, and only the 5v voltage output is used to ensure that the old USB powered device can work safely.
Features:Support for Class A and Class B specifications of QuickCharge 3.0
USB charging interface intelligent recognition
Apple2.1A/2.4A
SamsungGalaxyNote2.0A
BC1.2&YD/T1591BatteryChargingSpecifications
4kVESD
-40~125°C°C operating temperature range
Power consumption as low as 1mw at 5V output
CX7918 package form SOP-8; CX7916 package form SOT23-6

USB-PowerDelivery (USBPD) is a protocol specification that supports up to 100W of power and data communications in a single cable. USBType-C is a new front and back plug-in USB connector specification that supports a new set of standards such as USB 3.1 (Gen1 and Gen2), DisplayPort and USBPD. The USBType-C port supports up to 5V3A by default. If the USBPD is implemented in the USBType-C port, it can support the 100W power (5V20A) defined in the USBPD specification. Therefore, having a USBType-C port does not mean it supports USBPD.
Our interactive touch foil is a new, transparent touch film ,with high accuracy ,easy to install on the glass,Acrylic ,or PC.It widely uesd to shipping mail,Education ,Exhibition,Hotel ,Airport etc.Our company is a top level company which grasp the technology for capacitive touch foil.capacitive touch foil is also called "touch film", nano touch foil, which is a grid matrix layer composed of two thin films with a layer of X and Y axis interlaced nanowires.It can through the glass or other objects to touch just like gesture.These smart touch foil by customers love and satisfaction.
pictures show:





Multi Touch Foil,Capacitive Touch Foil,Projection Touch Screen Foil,Nano Touch Film,Touch Foil with Controller,USB Capacitive Touch Film
ShenZhen GreenTouch Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.bbstouch.com
